Acid-Base Properties of Amino Acids
Investigate the pH-dependent protonation of amino acids.
Tasks
- Create and optimize a glycine molecule (\(\ce{H2N-CH2-COOH}\)). Open
Build Menuand selectAdd Hydrogens for pH...Choose different values of pH : 1,2,3,…,13 and note the effect of pH shift on electrical charge of glycine. - In a new View, create a (Glutamic acid - Lysine) dipeptide using
Build Menu>Insert>Peptides...Set pH to 3 and calculate the correspondent electrical charge of the dipeptide. Do the same for pH=7 and 13.
When performing a paper electrophoresis at these pHs, in which direction will the dipeptide move (anode or cathode) ?
Solution
- Glycine electrical charge according to pH shift:
- pH<5: \(\ce{NH3+-CH2-COO-}\) \(\ce{H+}\); net charge =+1
- 5≤pH<10: \(\ce{NH3+-CH2-COO-}\); net charge =0
- 10≤pH≤13: \(\ce{NH2-CH2-COO-}\); net charge =-1
- Glu-Lys dipeptide:
| pH | 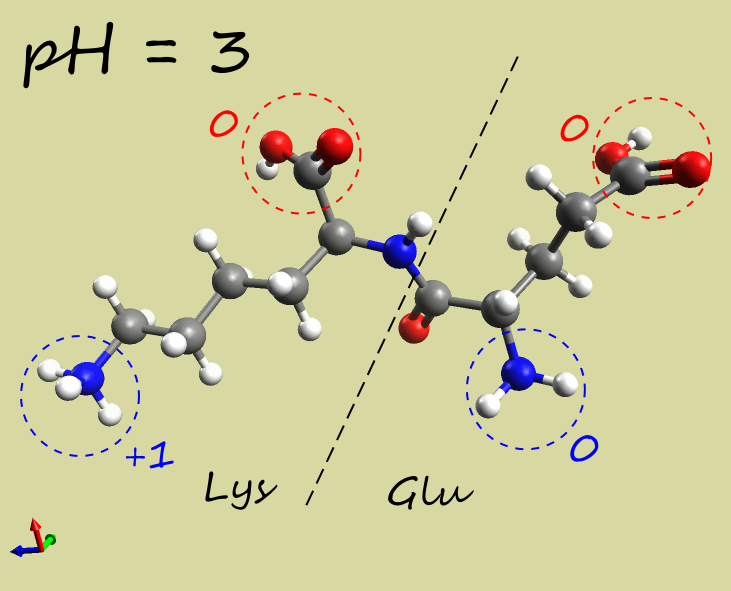 |
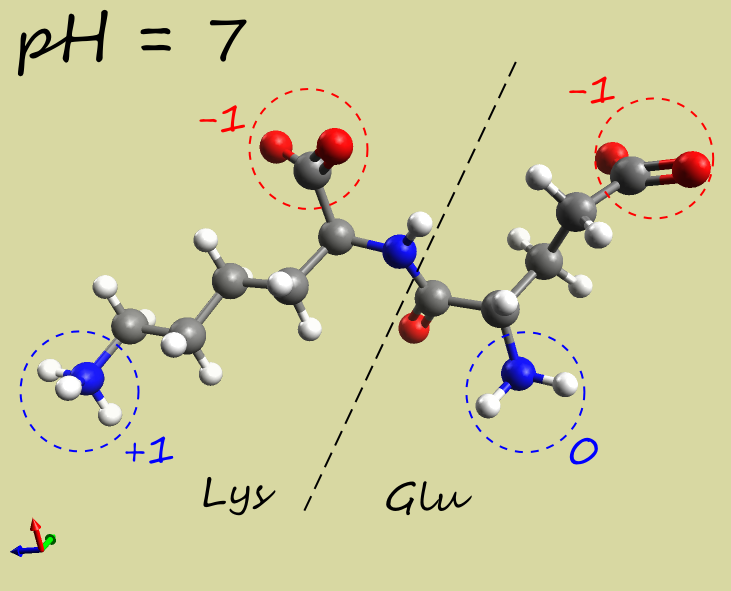 |
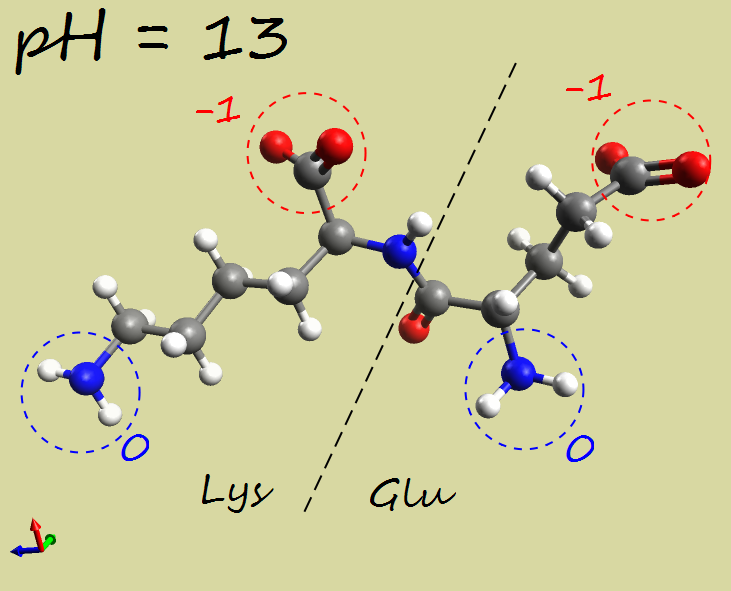 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Net charge | +1 |
-1 |
-2 |
| Electrophoresis | → cathode (−) | → anode (+) | →→ anode (+) |

Comments